TEL:
+86-0312-3189593
 English
English

Telephone:0312-3189593

Email:sales@oil-tester.com
2 月 . 13, 2025 12:37
Back to list
power transformer oil testing pdf
Power transformer oil testing is an indispensable practice for maintaining the integrity and performance of transformer systems. As an essential component in the electrical power industry, transformer oil serves as both an insulator and a cooling medium. Over time, the oil can degrade, leading to potential transformer failures if not adequately monitored and managed. Therefore, understanding and implementing routine oil testing is crucial for ensuring operational efficiency and longevity of transformer equipment.
Beyond individual test parameters, comprehensive transformer oil testing aligns with more extensive condition monitoring strategies. Adopting an effective oil testing regime can significantly extend the operational life of transformer units, mitigate unexpected failures, and reduce maintenance costs. For organizations relying on power transformers, implementing regular oil testing is not just a recommendation but a requirement for efficient asset management. Expertise in power transformer oil testing not only involves understanding the tests themselves but also interpreting the results accurately. Transforming test data into actionable insights depends upon a nuanced understanding of both the equipment’s operational history and the industry-specific norms. Ensuring authoritativeness in transformer oil testing processes involves engaging certified testing laboratories. Often, such institutions are accredited and employ standardized test methods, ensuring consistent and reliable results. This credibility translates into actionable data that organizations can rely on for strategic decisions regarding their transformer fleet. Moreover, integrating trustworthiness within oil testing protocols enhances stakeholder confidence. Transparency in testing procedures, clear communication of results, and prompt implementation of mitigation strategies when anomalies are detected establish a foundation of trust, not only within teams responsible for transformer maintenance but also among clients and partners. Overall, the importance of transformer oil testing cannot be overstated. For entities both large and small, overlooking this critical aspect of transformer maintenance can lead to costly downtime and repair expenses. By leveraging expertise and maintaining a proactive service schedule, grounded in authoritative and trustworthy practices, organizations can ensure the seamless operation of their power systems, reinforcing reliability and safety across all operational levels.
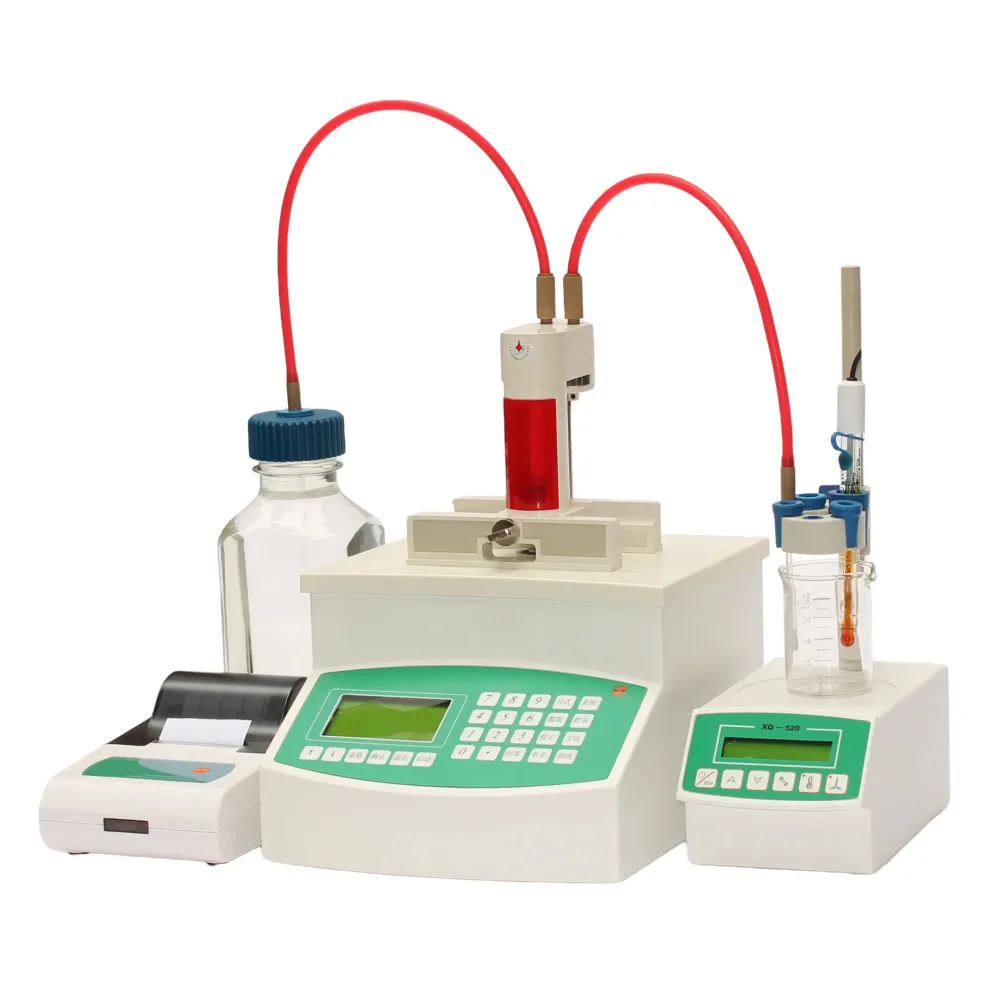

Beyond individual test parameters, comprehensive transformer oil testing aligns with more extensive condition monitoring strategies. Adopting an effective oil testing regime can significantly extend the operational life of transformer units, mitigate unexpected failures, and reduce maintenance costs. For organizations relying on power transformers, implementing regular oil testing is not just a recommendation but a requirement for efficient asset management. Expertise in power transformer oil testing not only involves understanding the tests themselves but also interpreting the results accurately. Transforming test data into actionable insights depends upon a nuanced understanding of both the equipment’s operational history and the industry-specific norms. Ensuring authoritativeness in transformer oil testing processes involves engaging certified testing laboratories. Often, such institutions are accredited and employ standardized test methods, ensuring consistent and reliable results. This credibility translates into actionable data that organizations can rely on for strategic decisions regarding their transformer fleet. Moreover, integrating trustworthiness within oil testing protocols enhances stakeholder confidence. Transparency in testing procedures, clear communication of results, and prompt implementation of mitigation strategies when anomalies are detected establish a foundation of trust, not only within teams responsible for transformer maintenance but also among clients and partners. Overall, the importance of transformer oil testing cannot be overstated. For entities both large and small, overlooking this critical aspect of transformer maintenance can lead to costly downtime and repair expenses. By leveraging expertise and maintaining a proactive service schedule, grounded in authoritative and trustworthy practices, organizations can ensure the seamless operation of their power systems, reinforcing reliability and safety across all operational levels.
Previous:
Latest news
-
Differences between open cup flash point tester and closed cup flash point testerNewsOct.31,2024
-
The Reliable Load Tap ChangerNewsOct.23,2024
-
The Essential Guide to Hipot TestersNewsOct.23,2024
-
The Digital Insulation TesterNewsOct.23,2024
-
The Best Earth Loop Impedance Tester for SaleNewsOct.23,2024
-
Tan Delta Tester--The Essential Tool for Electrical Insulation TestingNewsOct.23,2024





